The team is sitting in a meeting in silence—no solution to the problem in sight? Brainstorming can help you avoid this creative void. The group activity gets the ideas flowing, and the team can choose the right one together.
There are several brainstorming methods you can use. In this article, we will look at different brainstorming techniques, help you choose one, and give you some practical tips and tools.
What is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a creative technique that can help generate ideas. Although some of the methods are suitable for individuals, most are designed for groups. When the team is faced with a problem or wants to advance the development of a product, brainstorming can help find an appropriate solution.
Brainstorming is a problem-solving technique in which a group collects ideas and suggestions for solving a particular problem.
The term brainstorming was coined by Alex Osborn in 1939. He was looking for a way to create a creative environment in which ideas could be generated. He based his term on the English translation of the Indian mantra “using the brain to storm a problem.” This coined the term brainstorming, which is in common use today.
However, to create a brainstorming environment that actually encourages the generation of ideas, you should follow a few rules.
Rules for Brainstorming
When you want use brainstorming methods with your team, the number of people involved can make it difficult. So before you start brainstorming, you should set some rules that apply to everyone in the group.
Basically, there should be only one moderator. He or she must be able to take charge but also create a good atmosphere in the group. All participants should feel equal and heard. This is the basic rule. To achieve this, the following additional rules are useful:
- Tolerance: The proposed ideas should not be judged. The focus is on collecting different ideas. This means that unconventional ideas can also find their place.
- Quantity instead of quality: The focus of brainstorming methods are to gather as many different ideas as possible. The more ideas you collect, the more likely it is that you will find the right one.
- Stealing ideas: All brainstorming methods should allow people to take ideas and think about them further or combine them. This can lead to new approaches.
- Be crazy: Far-fetched, unrealistic, and completely exaggerated ideas? There are no such things! Don’t be afraid to approach the problem from completely different directions and present unconventional ideas. The more unusual, the better, because it gives free rein to creativity. As a result, the solution may be in a direction that no one else has thought of.
Why Should You Brainstorm?
Brainstorming is often used in teams to quickly generate new ideas for a problem. It brings together people who can offer new approaches and perspectives. This makes it possible to solve a problem in a short period of time.
Brainstorming Methods: These Techniques Exist
Teams often use the traditional method of brainstorming, where many ideas are collected in a short space of time. In the brainstorming phase, ideas are mentioned and written down without further thought. Suggestions are not examined or filtered until later.
Let’s know all these brainstorming methods in detail.
Table of Contents
Depending on the goal or problem, other methods of brainstorming may be used.
1. Brainwriting
In Brainwriting, everyone in the group writes down their ideas on a piece of paper. They are given a certain amount of time to do this. When the time is up, they pass the paper to their neighbour, who writes down more ideas that build on the previous ones. This is the basic rule of brainwriting.
Brainstorming vs. Brainwriting
The term brainstorming encompasses all creative methods. Brainwriting is one of them. It is completely non-verbal.
2. Brain Netting
Brain Netting is a great solution for remote teams. Digital brainstorming uses a centralized platform. All ideas are captured in the online brainstorming tool.
In addition, a brainstorming tool for mind mapping can be useful as an online session to record, analyze, and develop suggestions.
The following tools and software are suitable for this purpose:
3. Mind Mapping
Similar to rapid brainstorming, mind mapping involves collecting ideas around a central theme. However, the thoughts that come up during brainstorming are categorized in a mind map. This makes the connections visible.
Mind mapping is the best among brainstorming methods for remote teams. Teams can use mind mapping not only on-site with a flipchart but also during online brainstorming or idea generation. Special online mind-mapping tools are available for this purpose, like:

4. Figure Storming
In this type of brainstorming, you approach a problem from someone else’s perspective. You do this by asking the team the question, “How would person XY solve this problem?” This could be someone from a different department, for example. Figure-storming is a good option if your team or group keeps coming up with the same ideas.
5. Round-Robin Brainstorming
As the name suggests, this creative brainstorming method starts with everyone sitting in a circle. The basic rule is that everyone takes turns coming up with an idea on the topic, and the moderator collects the suggestions. This approach or process has the advantage of getting everyone involved in the idea generation process.
6. Starbursting
Unlike other brainstorming methods, this technique does not collect ideas in bullet points but rather frames them as questions. The team works backwards to approach the problem. The questions make it possible to look at different aspects of the big picture and find ideas for the main problem.
A simple example of the starbursting technique is the launch of a new product. You and your team can approach the project by asking the following questions: Who will lead the different phases of the product launch? What is the target market segment?
7. Why Analysis
Why analysis is also based on the question principle. The moderator explains a problem, and the group or team asks five why questions to get to the bottom of the problem. This is a common and easy-to-use brainstorming method in project and quality management.
8. Reverse Brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming takes an entirely different approach from other brainstorming methods. Instead of finding a solution to the problem, this method looks for ways to cause the problem. Then the ideas are reversed: from the cause of the problem to the solution.
For example, a marketing team can use reverse brainstorming to figure out how to get fewer leads. The moderator might ask, “How would we intentionally generate fewer leads from our new product page?”
Some ideas could include:
- Make the user experience and page design difficult to use.
- Remove CTAs from your posts and pages to make it harder for people to contact you.
- Use boring or confusing language, images, or designs to convey your branding and messaging.
- Use pop-ups and forms that interrupt the customer’s web experience and make them less likely to call you.
9. The 6 Thinking Hats
This creativity technique was developed by Edward de Bono. The method of brainstorming involves participants taking on a role or hat and wearing it throughout the meeting. Each “hat” looks at the challenge, problem, or idea from a different perspective.
Edward de Bono distinguishes the following thinking hats:
- Analytical thinking (factual view)
- Emotional thinking (feeling-oriented view)
- Critical thinking (risk assessment)
- Optimistic thinking (opportunity-oriented view)
- Creative thinking (ideas)
- Organizing thinking (process view)
Other “thinking hats” can also be created for brainstorming, depending on what factors and considerations are important to the team and the organization.
For example, if the impact of an idea is particularly important, one participant “wears” that hat while another evaluates ideas from the customer’s perspective. As the meeting progresses, participants evaluate only from their own perspective. This way, the team can be sure that each idea has been considered from multiple perspectives.
10. The Stepladder Brainstorming
Best among brainstorming methods for introverts. This method takes some time, but it ensures that introverted participants have a voice and that the ideas of “loud participants” are not given more weight. This is how the stepladder works:
- The brainstorming topic is introduced.
- All but two participants leave the room. The people outside can work on their own ideas, but are not allowed to share them with each other. The two team members in the room, however, begin to explain and discuss the ideas with each other.
- Another participant enters the room and presents his or her idea. Only then do the three of you discuss the other ideas.
- This process is repeated until everyone is back in the room and can make a collective evaluation of all the ideas.
This brainstorming method works well for larger groups. However, to ensure that it runs smoothly, the appropriate conditions should be created.
Also Read:
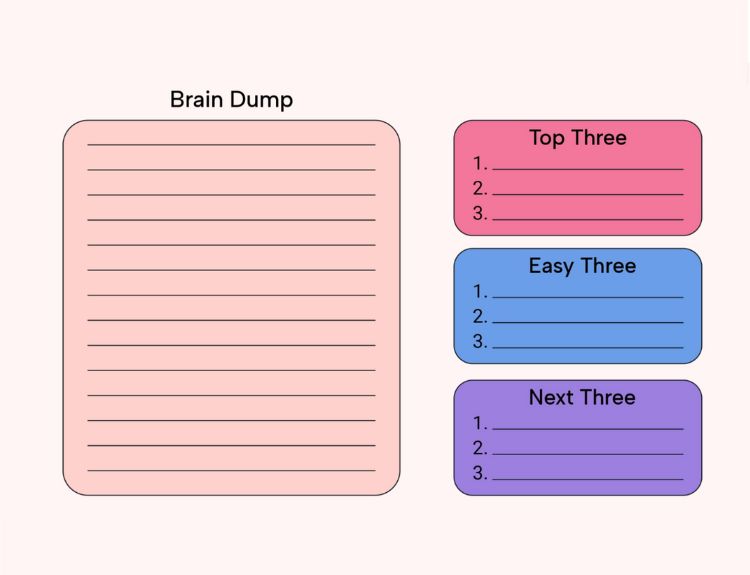
Brain Dump Method: A Simple Method That Helps Untangle Chaos in Entrepreneurs’ Head
Process of a Brainstorming Session
Regardless of which brainstorming method you use with your team members, there are a few things to keep in mind when brainstorming, because team members may not always come up with creative ideas or be able to develop them.
- To get good ideas, the question should be as clear and specific as possible. This will ensure better and more focused results. It is best for the facilitator to have the participants confirm that they have understood the question or problem.
- It is a good idea to start with a warm-up exercise. Team members need to disconnect from their recent tasks and reduce any stress. A simple warm-up game will loosen up the participants so that they can then participate in the brainstorming session and not think about other issues.
Warm-up exercise: alternative use
The Alternative Use Exercise is a good warm-up exercise. Here, you choose an object. For example, it could be a pencil. The participants’ task is to come up with alternative uses for the object. The ideas are then presented.
Just as important as incorporating a warm-up exercise into a session is scheduling breaks. To maintain creativity and concentration, you need to take regular breaks. Good results are often seen in the second or third round.
It is also possible to spread the brainstorming sessions over two days. Sometimes even better ideas come up in the evening, which can be discussed in the group the next day.
Breaking Down Barriers
If you suspect before the brainstorming session that some participants are afraid to express their thoughts, give the team the opportunity to write down their ideas as they brainstorm. In your moderation, you can also address unconventional ideas and encourage people to come up with crazy ideas.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Brainstorming
Brainstorming methods are very versatile and can help your team generate a lot of ideas. This creativity technique has both pros and cons:
Benefits of Brainstorming
- Generates multiple ideas simultaneously or helps refine ideas.
- Encourages creative thinking and can break entrenched thinking patterns.
- Promotes teamwork and a sense of inclusion for introverts in the office.
- Facilitates a quick and effective way to solve problems.
- Visualizes and structures thoughts for easy and creative solutions.
- Helps take multiple perspectives and look at a problem from different angles.
- Brainstorming can help overcome creative blockages.
Possible Disadvantages and Limitations of Brainstorming
Participants may not concentrate on brainstorming but only on the details of a particular idea (anchoring effect).
- A moderator needs to control the process.
- Too many ideas can create chaos or overwhelm.
- Many “side ideas” are generated that cannot be used.
- Introverts may feel uncomfortable in the group dynamic process.
- There may be potential for conflict when opposing opinions clash.
The disadvantages especially show that brainstorming needs a certain framework and control. Also, these disadvantages can then be mitigated through targeted moderation and the use of the right method.
Brainstorming Tools
Whiteboards and meeting rooms are useful but no longer a prerequisite for effective brainstorming: In practice, there are several tools available to take this process into the digital world. The biggest advantage is obvious: all notes and ideas are documented and stored online at the same time.
There are countless tools that can be used in your brainstorming sessions (depending on the method). These include:
- Mindmeister.com
- Lucid.app
- Miro.com
- XMind.app
- MindMup.com
- MindNode.com
- Whimsical.com
- Mapify.so
- Mymap.ai
However, a dedicated tool for any brainstorming methods is not required: sometimes a OneNote notebook is enough to capture ideas together.
Conclusion
Brainstorming is a creativity technique that uses different methods to generate ideas and overcome mental blocks. It helps the team look at a problem from different perspectives and work together to find a solution.
There are countless brainstorming methods, each with a different approach. The most popular are mind mapping, brainwriting, and starbursting. However, to ensure that the brainstorming process does not end in chaos, a moderator should control the process and make sure that the phases and rules of brainstorming are followed. This way, nothing gets in the way of creative idea generation.

Pingback: 111+ Interesting AI Tools for Startups